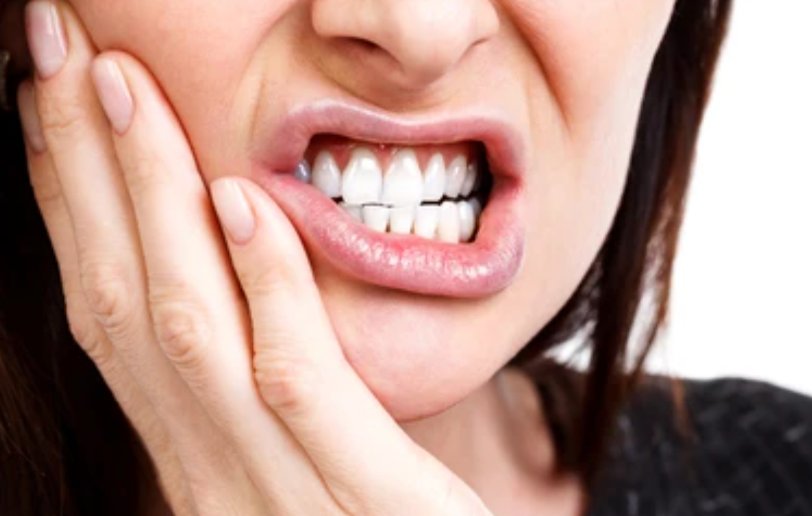
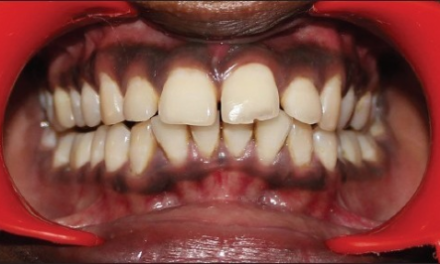
If you have a painful, swollen, and/or tender area in your mouth, it may be a sign of an abscess tooth. This dental problem occurs when a bacterial infection develops inside or around a tooth, leading to the formation of a pus-filled pocket. If left untreated, it can also lead to complications, such as bone loss, tooth loss and systemic infections. It is therefore crucial to seek dental care as soon as possible if you suspect you have an abscess around the tooth that is worrying you.
Symptoms of Abscess Tooth
- Fever
- Bad breath
- Difficulty chewing
- General discomfort
Causes of Abscess Tooth
- Gum disease that causes the gums to recede and the teeth to loosen, creating spaces for bacteria to invade
- Poor dental hygiene that allows bacteria to grow and multiply in the mouth
- Tooth decay that exposes the inner pulp and nerves to bacteria
- Trauma to the teeth or gums that can break or dislodge them, leading to bacterial invasion
- Medical conditions that weaken the immune system, such as diabetes or cancer, making it harder for the body to fight infections
Types of Abscess Tooth
- Periapical abscess: When a bacterial infection affects the tip of the tooth’s root, usually due to untreated decay or trauma.
- Gingival abscess: When a bacterial infection affects the gums, often due to trapped food particles or foreign objects that irritate the gums.
- Periodontal abscess: When a bacterial infection affects the deeper structures that support the teeth, such as the bone and ligaments, usually due to advanced gum disease.
- Dental abscess: A general term that encompasses all types of abscess tooth, regardless of their location or cause.
Treatment Approaches for Abscess Tooth
- Drainage of the abscess: A dentist will make a small incision or puncture in the abscess to release the pus and relieve the pressure, which can also reduce pain and swelling.
- Antibiotics: A dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help kill the bacteria and prevent the spread of infection, especially if the abscess is severe or systemic symptoms are present
- Root canal therapy: A dentist may perform a root canal if the abscess has affected the tooth’s pulp and nerves, which involves removing the infected tissue, filling the space, and sealing the tooth to prevent reinfection.
- Extraction: In some cases, a dentist may need to extract the affected tooth if it’s too damaged or infected to save, which can also prevent the spread of infection to other teeth and gums.
Summary
- This is a serious dental problem that requires prompt and professional treatment by a dentist.
- Remember to practice good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing daily and visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings.
- Don’t ignore any signs of dental pain or discomfort, as they can indicate a more significant problem that needs attention.